Manufacturers ask, “Is resin plastic?” because resins are made from a versatile material known as polymers, and new types of polymers and blends enter the market frequently. Resins give packaging materials strength, durability, and flexibility, so we can use different types of resin and plastic in packaging. Different types of resin have different characteristics. The uniqueness of each plastic is what yields different kinds of packaging applications.
Some confusion has emerged regarding the identification of the plastic resin identification codes (RIC). Maybe because the RIC looks so similar to the universal recycling symbol, people began to think that all plastics are recyclable, or they all shared the same characteristics. To prevent production errors, manufacturers have become knowledgeable about the types of resin and plastics. Choosing a plastic material has become a challenging task as manufacturers need to understand terms like amorphous, semi-crystalline, and additives to truly understand how to choose the materials that will give the desired properties. So, is resin plastic?

What Is Resin?
Resin is the most central ingredient in all plastic products. Resin is a semi-solid, versatile raw material that can be converted into a polymer. Polymers are converted into plastics.
With the addition of additives to improve the characteristics of the material, resin changes from semi-solid or liquid to a solid with varying degrees of rigidity. It is remarkable that by changing the chemical composition, such as causing short polymer chains to form long chains, a liquid can become a highly durable plastic material.
Properties of Resin
Understanding resin and plastic is important because plastics and resins are part of most products and packaging we use today. Plastic manufacturers manipulate these properties to produce endless possibilities in plastic products:
Original state: Resins are solid or semisolid.
Morphology: The arrangement of molecules in a resin is amorphous or semi-crystalline
Fusibility: Resin is fusible – it can be bonded with another material or chemicals.
Flammability: Almost all resins are flammable
Natural or synthetic: Natural resins typically come from plants. Synthetic resins are produced from chemicals.
Appearance: transparent or translucent
Solubility: Resins are insoluble in water; they are soluble in certain solvents.
Using Additives to Improve Types of Plastic
Chemicals are added to resins or processed to make them into thermoplastics or other types of plastic.
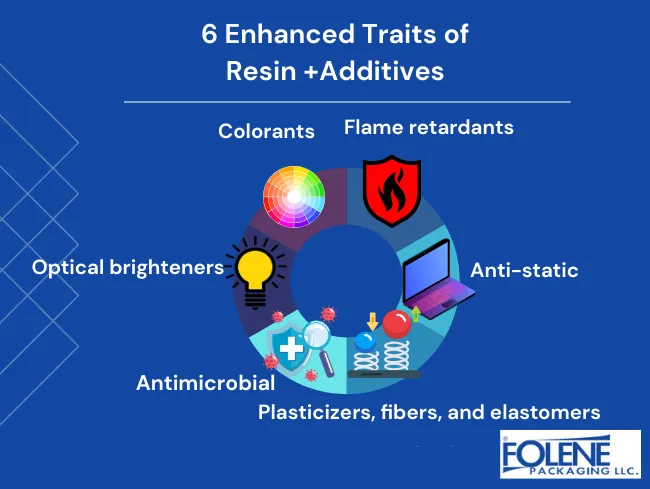
Additives enhance resins by strengthening them or adding new traits:
Antimicrobial – for food-related uses; keeps products that are handled a lot hygenic.
Anti-statics – for electronics; reduces the ability to conduct static electricity.
Plasticizers, fibers, and elastomers change the plastic’s form to be more pliable, stiffer, or elastic.
Flame retardants change the material from flammable to resistant to combustion.
Optical brighteners – improve whiteness and give a bluish-white glaze to plastics, paints, and inks.
Colorants – manufacturers can change the material’s color and add special effects to various types of plastics, making the product fluorescent or pearlescent
Is Resin Plastic?
Resin is not the same material as plastic, although they are definitely closely related. What we call plastic resins are types of plastic, and resins are natural or synthetic raw materials.
Is resin a plastic? No, although they are called resin codes for plastic, the resin itself – the natural or synthetic material – is not listed as plastic. We borrow the term resins generally in plastic making to refer to the raw soup that will become plastic products. In that sense, resin is plastic. Resins offer advantages over traditional materials.
Let’s look at the differences between resins and plastics.
Resin vs Plastic – 10 Comparisons
There are clear differences between resins and plastics:
Resins:
Resin is a general term that refers to materials obtained from synthetic or plant origins.
Resin is unprocessed plastic; a precursor to plastic. Natural resins are biodegradable.
Resin is versatile; it can be polymerized to form different plastic materials.
Resin can be cured by heating or adding a curing agent – just once.
Even pure natural resin can be used, such as for embedding decorative items and for coating furniture
Resin uses are limited: coatings, adhesives, and sealants.
Epoxy resin is a type of synthetic resin that is commonly used in coatings and adhesives.
Resin is a semi solid or a viscous liquid.
Resin cannot be recycled indefinitely.
Natural resins come from plants, such as pine resin, while petrochemicals are the source of synthetic resins.
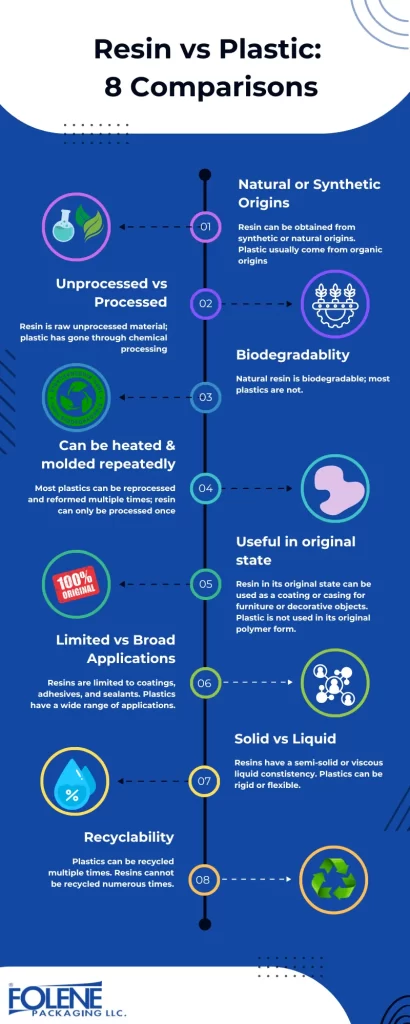
Plastics:
Plastics in the form of long-chain polymers must be derived from organic materials, including petrochemicals, cellulose, salt, crude oil, and plant-based substances such as vegetable oil.
Plastic is a synthetic or semi-synthetic material with polymers as its main component produced through chemical reactions.
Plastic is not found in a pure form.
Processed plastic is derived from recipes of resin mixed with different substances.
Plastic is the name we use to refer to the raw material produced from resin (synthetic polymers).
Plastic is used to produce many different types of plastic products. Plastic is an extremely versatile material. Some plastics can be melted and reformed multiple times without reducing their mechanical properties.
Plastics are not biodegradable. Production and disposal of plastic contribute to environmental pollution.
Plastic can be recycled. Some types of plastic can be recycled indefinitely.
Plastic cannot be converted to a different material; it can only be applied for use in packaging, construction, and consumer products.
Plastic products can be rigid or flexible, durable or brittle.
7 Types of Plastic: What Are The Different Types of Resin?
We use RIC resin Identification Codes to identify each different type of resin. Of course, the production of plastic is regulated by standards set by ANSI, which ensures the safety of plastic materials and oversees risk assessment for manufacturers.
These are the plastic resin codes for the various types of plastics:
RIC Number 1 -PETE – Polyethylene Terephthalate
It is commonly used for disposable food containers, storage jars, soft drinks, and water bottles.
RIC Number 2 – HDPE – High-Density Polyethylene
It is commonly used for shopping bags, flower pots, and soft cosmetics containers such as shampoo bottles.
RIC Number 3 -PVC – Polyvinyl Chloride
It is commonly used for pipes, plastic sheets, pool covers, and non-food product bottles.
RIC Number 4 -LDPE – Low-Density Polyethylene
It is commonly used for flexible food-related packaging such as bread bags, trash bags, and freezer bags.
RIC Number 5 – PP – Polypropylene
It is commonly used for rigid food-related packaging such as yogurt tubs and cups, shipping bags, and woven and non-woven plastic bags.
RIC Number 6 – PS – Polystyrene
It is commonly used for stiff and shiny disposable plasticware, takeaway containers, flatware, rigid clear plastic such as CD cases, foam cups, and foam packaging.
RIC Number 7
It is commonly- Other – This type of plastic includes all other types of plastic, including some specialty types of plastic such as polycarbonate (PC), nylon (also known as polyamide, PA), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), and plastics containing acrylic.

3 Ways Resin and Plastic Contribute to Packaging
Once processed into usable materials, resin and plastic are an inseparable duo. Resins in packaging offer unique advantages:
1. Resin plastic is stable and displays predictable chemical qualities.
It can be molded, called, and used at a predictable temperature. These qualities make working with plastic resins as a raw material straightforward and allow manufacturers to produce top-quality packaging materials.
2. Plastic resin can be economical.
The advantages that resin offers manufacturers and suppliers all along the supply chain allow substantial savings. By understanding the qualities of plastics, manufacturers can take advantage of plastic resins to save on storage space, delivery costs, and disposal charges. Plastic’s benefits include being lightweight, highly durable, and cost-effective.
3. Plastic resin identification codes help us know which plastics can be recycled
Understanding resins and different types of plastic allows our plastic-hungry world to source recycling scrap. Without the plastic scrap that indicates resin codes, the recycled resins used to produce packaging with recycled content could be produced. That would result in ever-increasing landfills.
Folene Packaging are Shrink Packaging Experts
Folene Packaging knows that the best way to answer any question about plastics and types of resin is to speak to the experts. Folene Packaging are experts on understanding plastic types and we use this knowledge to produce the highest quality shrink film for all packaging applications.
When choosing packaging types, resin, and plastic are not what you choose. You choose products, such as shrink wrap. Make sure to choose a shrink wrap that will hold your products safe and secure unitl the end of the supply chain – the end-user opens that package and finds the product intact and ready to use. For this, make sure to evaluate the requirements of your packaging needs. Use shrink film that is strong enough to protect your products, clear enough to showcase them, and sustainable enough for the end user to dispose of eco-consciously.
Contact Folene Packaging today to discover how we turn types of resin into high performance plastic shrink films that meet your plastic packaging needs.



