
What is Crosslinked Film, and How Does it Compare to Non-Crosslinked Film?
When selecting the perfect shrink film for packaging your products, one of the main decisions to make is between crosslinked film and non-crosslinked film. What is crosslinked film and what benefits does it offer? How does it compare to non-crosslinked film? And most importantly, how do you choose the best shrink film for packaging your products? Folene Packaging presents everything you need to know about crosslinked film vs noncrosslinked film so you can make an educated decision for packaging your products.
What is Crosslinked Film?
Crosslinked film, or irradiated film, is shrink film that has been through a crosslinking procedure to strengthen the bonds between the plastic polymers. The film is exposed to high levels of specific UV light waves that cause bonds to form and strengthen between the polymers, resulting in a stronger more durable shrink film product than before.
What is the Crosslinking Procedure?
Here is an overview of the general crosslinking process
Selecting the Film Base We begin with regular shrink film, either made from polyethylene or polyolefin, with the desired dimensions and gauge. The irradiation process won’t change the starting dimensions.
Additives Inclusion To enhance the crosslinking process, various additives may be incorporated into the film, including radiation sensitizers, which help improve the efficiency of the crosslinking process, or other additives that can further augment the film’s desired properties.
Irradiation Process The film is then exposed to a radiation source, commonly electron beam (EB) radiation or gamma radiation. The choice of radiation type depends on specific production requirements and the desired extent of crosslinking. The irradiation process occurs in a controlled environment, where the intensity and duration of exposure are carefully monitored to ensure effective crosslinking while preventing degradation of the material.
s Electron Beam (EB) Irradiation: In this method, high-energy electrons are generated and directed onto the film, causing the polymer chains to break and reattach, forming crosslinks. EB irradiation is known for its fast processing time and ability to penetrate materials uniformly. – Gamma Radiation: This method uses high-energy gamma rays, often sourced from cobalt-60 or cesium-137 isotopes. The gamma radiation penetrates deeply into the film, promoting crosslinking throughout its thickness, although processing times may be longer compared to EB.
Post-Irradiation Treatment Then is the cooling or additional processing to stabilize the newly crosslinked structure. This step is crucial to solidify the chemical changes to the polymer chains in the film, ensuring the film retains its enhanced properties during use.
Quality Control and Testing After completing the crosslinking process, the film undergoes rigorous quality control packaging testing to assess its properties, such as tensile strength, tear resistance, and clarity. Manufacturers may conduct these tests to ensure the film meets industry standards and specific application requirements.
What are the Benefits of Crosslinked Film?

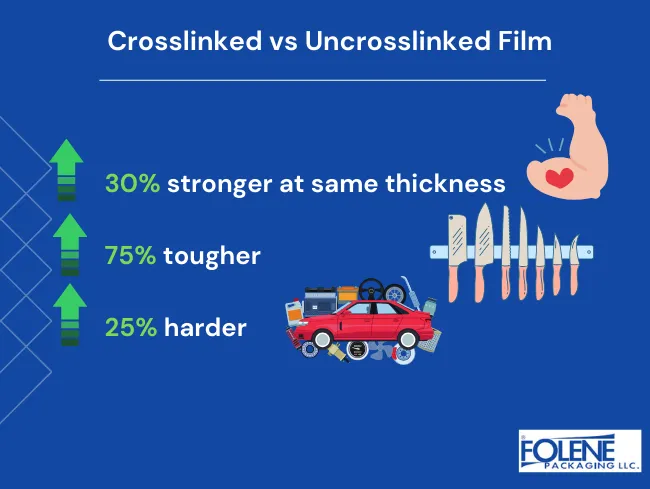
1. Stronger Tear Resistance
Crosslinked polyolefin shrink film demonstrates exceptional tear resistance compared to standard shrink films. This strong resistance minimizes the risk of punctures and tears during handling, storage, and transportation. As a result, products packaged with this type of film have a lower likelihood of damage, which can translate into cost savings and enhanced protection for the contents.
2. Better Clarity and Gloss
This shrink film offers superior optical clarity, which enhances the presentation of packaged products. This clarity allows consumers to have a clear view of the product inside, potentially increasing appeal and sales. Additionally, the gloss finish can make the product look more polished and professional, contributing to a positive brand image.
3. Higher Heat Resistance
Crosslinked polyolefin films can withstand higher temperatures without compromising their integrity. This characteristic makes them suitable for applications that require heat sealing or exposure to temperatures that typical shrink films cannot handle. As a result, this property allows for more flexibility in packaging processes and better protection during transportation.
4. Enhanced Puncture Resistance
The crosslinking process enhances the physical properties of the film, making it more resilient to punctures. This is particularly beneficial in industries where the packaged products might be subject to rough handling or where sharp edges could potentially damage the packaging. Enhanced puncture resistance ensures that the products remain safely enclosed, reducing waste.
5. Suitable for High Abuse Applications
The durability of crosslinked polyolefin shrink film makes it ideal for high abuse applications, such as those seen in industrial environments. Items need to endure rigorous conditions without compromising the package integrity. This robustness ensures that products remain safe and secure during shipping and handling even in challenging conditions.
6. Versatile Applications
This type of shrink film can be used for a wide range of applications, including food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and industrial products. Its versatility stems from its ability to adapt to various packaging needs without losing performance. This means manufacturers can use a single type of film for multiple products, simplifying their inventory management.
What are the Drawbacks of Crosslinked Film?
Despite the many benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider when using crosslinked polyolefin shrink film:
1. Cost
Crosslinked films tend to be more expensive than standard shrink films due to the complexity of their manufacturing process. This increased cost can be a significant factor for companies operating on tight budgets. While the benefits may justify the expense for some applications, it could deter cost-sensitive businesses from using this material.
2. Environmental Concerns
Due to the chemical changes the film undergoes during the crosslinking procedure, this type of film is not as easily recycled compared to noncrosslinked films. This can be a major drawback for companies, depending on their packaging needs and ideals.
Crosslinked polyolefin shrink film offers numerous benefits that make it a valuable choice for various packaging needs. However, it’s essential to weigh these advantages against potential drawbacks to determine if this material aligns with specific production requirements and budget constraints.
How does Crosslinked Film Compare to Non-Crosslinked Film?
Non-crosslinked films, also called standard or conventional shrink films, offer several key advantages over cross-linked films:
- Cost-Effectiveness
Non-crosslinked films are generally less expensive to produce than crosslinked films. This affordability allows businesses to save on material costs, making them appealing for companies operating within tight budgets. They offer an economical solution for many packaging needs without compromising on basic performance.
2. Ease of Processing
Standard shrink films are typically easier to handle and process during manufacturing. They can be sealed and shrunk using conventional heat-sealing techniques and shrink film equipment without requiring specialized equipment or processes. This simplicity can lead to shorter production times and reduced complexity in packaging operations.
3. Good Shrink Characteristics
Non-crosslinked films exhibit effective shrinkage when exposed to heat, offering a tight fit around products. This characteristic is essential for maintaining product visibility and ensuring the contents are securely packaged. The ease of achieving the desired shrinkage makes these films ideal for a variety of consumer and industrial applications.
4. Equipment Compatability
Non-crosslinked films are not universally compatible with all types of equipment and require specific V-Knife blades in order to run smoothly on machinery. Crosslinked film is universally compatible with all types of equipment, reducing the headache and initial investment for manufacturers who want to make the switch to crosslinked film.
5. Transparency and Clarity
Many non-crosslinked films are designed to offer high levels of transparency and clarity, allowing the packaged products to be easily seen. This visual appeal can enhance product marketing and consumer interest. As a result, businesses can present their products in an attractive manner, potentially increasing sales.
6. Low-Temperature Compatability
Non-crosslinked films tend to perform well in low-temperature environments, maintaining their integrity without becoming brittle. This quality makes them suitable for use in refrigerated or frozen food packaging, as well as in other markets where low-temperature stability is essential.
7. Reduced Environmental Impact
Noncrosslinked films have a lower environmental impact. For example, all of Folene Packaging’s non-irradiated films are fully recyclable. Some non-crosslinked films are made from biodegradable or PCR materials, which can be beneficial for companies focusing on sustainable packaging solutions. By choosing eco-friendly options, businesses can enhance their corporate social responsibility profile and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Is Crosslinked or Non-Cross linked Film Better?
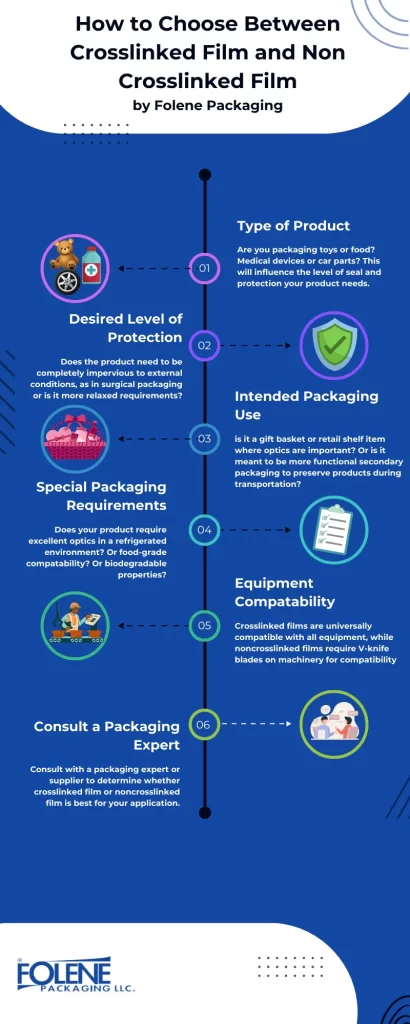
Crosslinked film and non-crosslinked films each have their pros and cons and are better suited to different packaging applications. Here are some of the key points to consider when deciding between these two types of film.
Non-crosslinked shrink films provide an array of benefits, including cost savings, ease of use, versatile applications, and appealing aesthetics. While they may not offer the same level of durability and resistance to abuse as crosslinked films, they serve as an effective solution for many standard packaging needs. Understanding the advantages of non-crosslinked films enables businesses to make informed choices based on their specific requirements and budget considerations.
Product you are Packaging
Level of protection required
Special Packaging Considerations- high or low temperatures, industry regulatory requirements
Packaging equipment- Cross linked films are universally compatable with all types of machinery, while noncrosslinked films are only compatible with V-knive machines. Mushroom blades and universal blades will not work with noncrosslinked films. Consider your packaging equipment and if replacing equipment is practical or cost-efficient.
Discuss your packaging requirements with a packaging product specialist, who can guide you to the best heat shrink film for your needs.
Conclusion
When choosing between crosslinked and non-crosslinked shrink films, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of your packaging application. Crosslinked films offer superior strength, tear resistance, and heat tolerance, making them ideal for high-demand environments and applications requiring robust protection. Conversely, non-crosslinked films provide cost-effectiveness, ease of processing, and versatility, which are beneficial for a wide range of standard packaging needs.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on the type of product being packaged, the level of protection required, any special packaging considerations, and the compatibility with your existing packaging equipment. Consulting with a packaging specialist can provide valuable insights and help you select the most suitable film for your specific requirements. By understanding the distinct advantages and potential drawbacks of each film type, businesses can make informed choices that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. Contact Folene Packaging today to determine the right shrink film for your products.



