
Manufacturers and distributors frequently face concern over supply chain disruptions. The smooth production, shipping, and distribution process relies on the continuous supply of raw materials and components. Sourcing disruptions mean that suppliers cannot provide raw materials to factories. The ripple effect travels to distributors and retailers, resulting in consumer shortages. Businesses can learn how a circular economy can support supply chain requirements.
Circular economy principles guide businesses as we shift from single-use to reusable packaging and minimize avoidable waste. We can learn about the effects of a circular economy approach on the supply chain from production to the consumer. As we change our consumption habits, we can avoid shortages that impact the supply chain.
What is the Circular Economy?
A circular economy seeks to reduce, reuse, and recycle materials and components whenever possible. It avoids the consumption of finite natural resources while encouraging economic activity through sustainable production and consumption. A circular economy model can guide our consumption to reduce waste and pollution in packaging and manufacturing while successfully regenerating natural systems.
The circular economy represents an effective response to environmental challenges, such as:
climate change
global greenhouse gas emissions
resource depletion
waste management
ecological degradation
It is easy to see that factors that impact the environment can also affect the supply chain.

3 Core Circular Economy Principles
Circular business models avoid extracting new materials; this is a transformation from the traditional linear economy. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation is very instrumental in publicizing the three principles of a circular economy, which are:
Eliminate waste and pollution: Instead of a take-make-waste system, since waste results from how we choose to design products, we can move from a linear economy to a more circular economy where we ask, “How can this be reused at the end of its useful life.” The resulting mass of waste and pollution is less.
Circulate products and materials: Keep reusing materials in their most helpful form—either as products, components, or raw materials. This is done through two amazing cycles – the technical cycle, where we apply “the 5 R’s” of circular economy to actual items (reuse, refurbish, repair, reduce, and recycle), and the biological cycle, where biological materials are broken down by composting or anaerobic digestion. Renewable energy is an example of non-finite resource consumption.
Regenerate nature: We replace “extracting” from nature with “regenerating” or supporting natural processes. By reducing the use of nonrenewable resources, pollution, and ecosystem damage globally, we can make healthy soils that absorb carbon emissions. These soils also hold water, helping to avoid droughts and flooding.
Thanks to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, there is increasing awareness that a circular economy is a functioning economic model. Following the three key circular economy principles can improve the supply chain. Through education, manufacturers will be equipped with circular economy strategies based on the latest research for a better transition to a circular economy model.

3 Ways Circular Economy Principles Can Improve the Supply Chain
Supply chain and sourcing disruptions can come from many sources. Some disruptions are from our natural environment, and some are man-made. The real question is how adopting circular economy principles can tackle these issues.
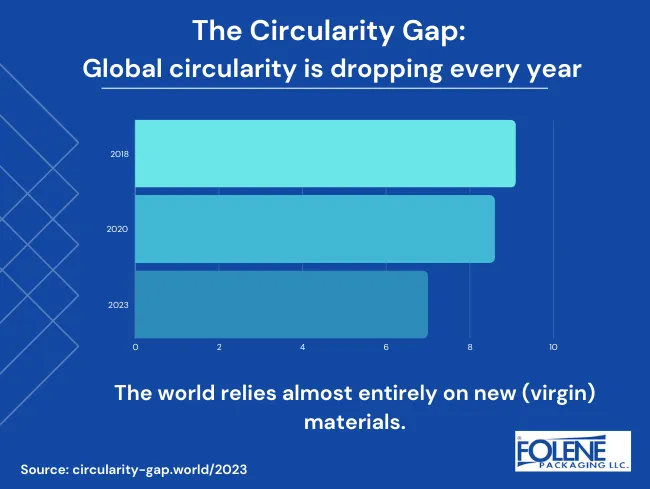
The Circular Economy Gap
The circular economy gap is a metric that tells us how much of the materials we use are recycled (currently 7.2%) versus how much materials we still need to use. Currently, all the materials we do not reuse (natural resource extraction and waste materials) constitute over 90% of the global supply. These either go to waste or are unavailable for reuse for a long time.
The circular economy gap is one factor resulting in an increased cost of raw materials and scarcity. The circular economy can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses and consumers by reusing materials so that we do not have to use “virgin” (new) materials. Resource efficiency extends the life cycle of products, makes raw materials more available, and could stall price increases.
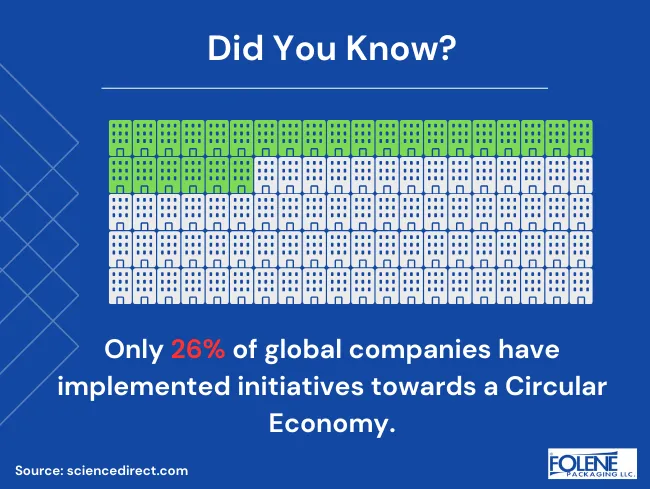
The Work of Circular Economy Companies
Manufacturers struggle to overcome a lack of raw materials due to a shortage of supplies (e.g., scarcity of wood due to deforestation), suppliers, and workers and due to a lack of natural raw materials from dwindling natural reserves. Besides the fact that many people work in technological and service industries, mining raw materials is challenging.
Producers grapple with compliance issues, environmental pollution, contamination, and inefficient production processes. As the number of circular economy companies increases, new business models seek to provide raw-reused materials by following circular economy principles. This creates new business opportunities, creates jobs, and powers economic growth. Job creation is noticeable, particularly in recycling, refurbishing, and sustainable product design.
The increase in circular economy companies also answers manufacturers’ demands for sufficient raw materials worldwide. One of the benefits of a circular economy is that it drives innovation, leading to the development of new technologies and business models that benefit our economic system, the industrial economy, and society.
Circular Economy Sustainability and Global Challenges
Supply chain disruptions can also occur because of transportation or logistics issues. Production processes based inside the country can avoid issues caused by traffic, shipping damage, and inclement weather delays.
The other side of the coin means that as we learn to get along better as a worldwide community, with joint goals of sustainability and circular economy, we can overcome supply issues caused by geopolitical events. Pandemics, natural disasters, political conflicts, or trade disagreements significantly impact the supply chain. They can cause supplier shortages and lead to fluxes in demand. By following circular economy principles, we will waste less and regenerate more.
The circular economy offers the global community a pathway to sustainable growth, ensuring long-term economic resilience. Additionally, it promotes social cohesion by encouraging collaboration and cooperation across different sectors and levels of government.
Circular Economy Examples
Companies That Welcome Circular Economy Benefits
Leading brands are increasingly adopting the circular economy concept. This has a supply-push effect, as the brands themselves want to reduce the waste production causes, and a demand pull, as consumers support companies that uphold a circular business model, reducing their carbon footprints.
The Sustainability Magazine (Apr 19, 2023) lists its top 10 circular economy companies—companies that value the benefits of a circular economy and have adopted circular economy aims. Their list includes leaders in the fashion industry and other leaders: Patagonia, IKEA, Unilever, Accenture, H&M, Adidas, Interfac e, HP, TrusTrace, and Mud Jean.
In the Electronics Industry: E-Waste Recycling and Refurbishment
Apple’s robot Daisy disassembles iPhones and mines valuable recyclable components. Apple aims to stop using any plastic packaging by 2025.
Dell’s closed-loop system recycles existing materials, recycles plastics from old computers into new ones, and aims to make 100% of its packaging from recycled or renewable materials; Dell plans to reuse packaging.
In the Food Industry: Circular Economy in Packaging and Waste Reduction
TerraCycle initiated “Loop,” which provides products in reusable containers. Consumers return the containers, and they are cleaned and refilled.
Many supermarkets and food companies continue to adopt circular economy principles by minimizing food waste.
A Linear Versus Circular Economy in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a significant contributor to waste and pollution, with a large amount of waste generated during the production and disposal of vehicles.
In a circular economy, sustainable practices will include designing vehicles for recyclability, using recycled materials, and promoting reuse and recycling.
Many companies are making commitments to follow circular economy principles. We will benefit from fewer shortages in chain supply and greater availability of materials. Circular economy principles ensure that supply chains within industrial systems are more resilient and adaptive. Manufacturers who act sustainably can enjoy the benefits of a circular economy and maintain regular customer supply capacities.
We can’t avoid all disruptions, but by adopting a circular economy and sustainability strategies, we can foster sustainable growth and greater flexibility in our habits as producers and consumers.



