
Packaging consumer durables can be challenging. Consumer durables can be large and bulky; they can be expensive or sensitive to environmental conditions. Suppliers of consumer durables need to understand how proper packaging can help ensure the products travel through the supply chain in perfect condition.
Proper packaging aims to prevent harm from coming to the items during shipping and warehousing, but there is much more to know about packaging for consumer durables. The requirements of the different parties along the supply chain need to be met. Think of the cost, ease of handling the products, and sustainability. In 2022, the U.S. durable goods sales revenue was about $5 trillion from $4.44 trillion in 2021, reflecting an increase in aggregate production in that sector. Investing in packaging options for durable consumer goods could be one of the factors that caused prices for durables to fall by 25% since 2000.
Consumer Durables – What Are They?
Consumer durables are also known as ‘hard goods’ and ‘durable goods.’ Consumer durables refer to products that do not wear out quickly; they don’t have to be replaced like consumer packaged goods – soft goods purchased frequently.
Consumer goods that last for at least 3 years are defined as durable by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis. Many retailers define durable goods: Products are durable if they come in rigid boxes, as that is one way many durable goods are packaged. Consumer non-durables come in packaging that is either rigid or flexible but less commonly in a box.
Durable Goods Examples
Examples of consumer durable goods are:
Large and small consumer electronics (such as washing machines, coffee makers, and computers)
Motor vehicles (such as new cars)
Office furnishings (such as desks and filing cabinets)
Camping equipment and other sporting goods (such as tents and helmets)
Air conditioners
Household goods and furniture that are designed to last for a long time.

What Kind of Packaging Do We Use For Consumer Durables?
Thanks to the invention of new packaging materials and new ways to use traditional packaging materials, packaging for consumer durable products comes in many different forms. Some varieties serve as primary packaging, and others as wrap pallets. Consumer durables companies must always fully understand the packaging product data sheet to apply the best type of packaging for the job.
Here are some typical packaging used for consumer durables:
Cartons and Boxes
Thick cardboard and paperboard containers are used for the interior and exterior packaging of durable goods. Use includes:
Boxes – the most popular cardboard shipping cartons can come in all sizes. They are used for shipping and aggregating smaller cardboard boxes for shipping.
Smaller cardboard or kraft paper boxes can have a clear plastic film window that lets customers see the product without touching it.
Self-locking cardboard boxes, such as those used for mobile phones, computers, and accessories, protect products by mandating an extra step before they can be accessed.
Boxes with flaps at the top and bottom that tuck in are used less for durables.
Sensitive electronics and gadgets, such as printer toner and ink cartridges, are sometimes supplied in lined boxes with metalized lining.
Buffers
Air-filled pillows, cushions, polystyrene peanuts, and bubble wrap protect irregularly shaped durable goods packed in a regular-shaped box. Fillers and padding are very common in the packaging of durable goods.
Other Cardboard
Cardboard tubes are sustainable containers for small electronics, wearable devices, and rolled-up paintings (art is a durable good as it rarely depreciates).
Cardboard pockets – act as envelopes to protect documents or prevent small components from getting lost.
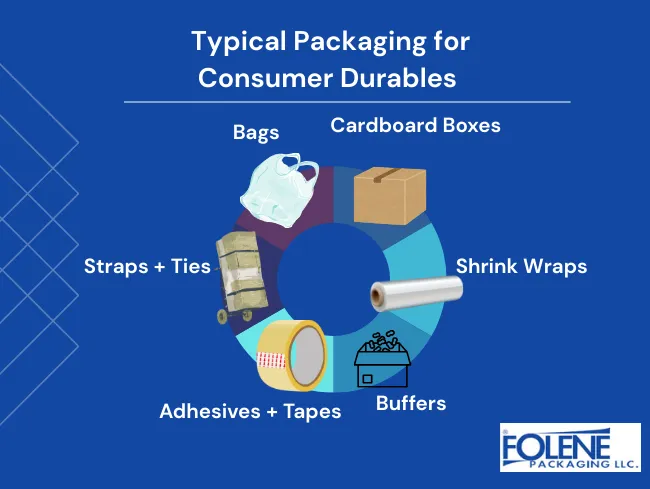
Wraps
Shrink wraps are transparent or opaque films that provide primary protection (i.e., they touch the product) against dirt, moisture, or sunlight. Wraps unitize components within a package (such as a remote control car, its batteries, and its handset). Shrink wrap over consumer durables is usually used in conjunction with other packaging.
Stretch wraps are used for palletizing and bundling consumer durables, such as for tertiary packaging (the most exterior packaging) in shipping cartons.
Straps and Ties
Metal straps made of tin and aluminum are used to lift heavyweight hard goods by forklift or to load cars onto auto racks.
Plastic straps of polyethylene, polyester, polypropylene, nylon, or rayon unitize loads, protecting the package against loss and theft. Straps also act as grips for easy handling.
Adhesives and Tapes
Tapes are essential for sealing boxes, aggregating individual products, and adding security above the outermost packaging, such as strengthening small boxes and bags that are not super-strong mailer bags.
Bags
Mailer bags offer lightweight delivery solutions, and padded soft envelopes offer added protection for mail delivery, drop-off delivery, and packaging of extra sensitive parts, such as electronics repair parts. Bags also provide insulation against contamination and moisture.
Why Do Consumer Durables Require Different Kinds of Packaging?
Packaging plays several important roles in the production of durable goods. The supplier, distributor, and retailer all need the packaging of consumer products to succeed 100% so that the consumer receives a perfect product – and to increase sales and profits.
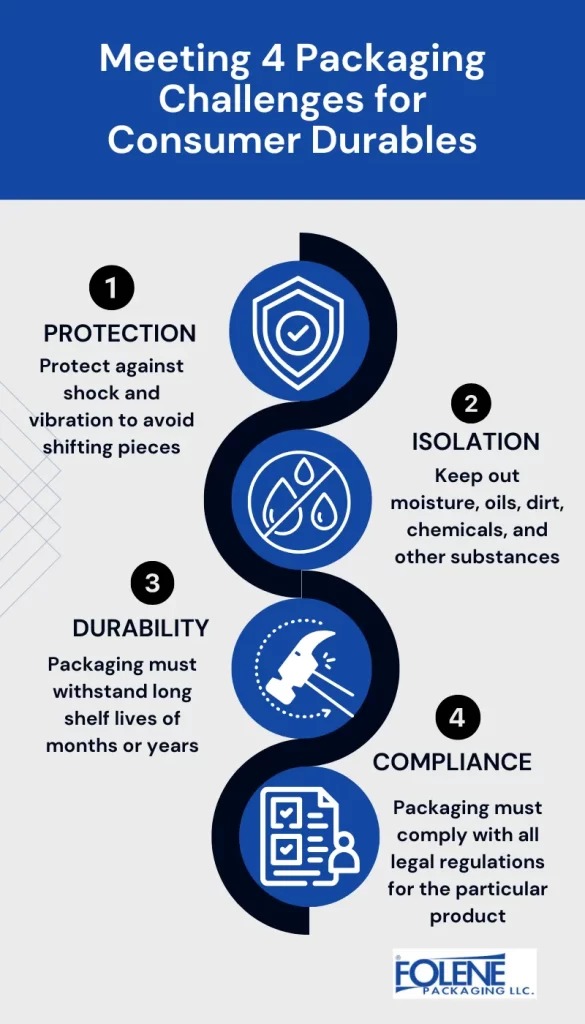
Packaging for consumer durables must offer:
1. Protection for consumer durables
Protect against shock and vibration and prevent the product and its components from shifting and damaging during longer storage times and transportation.
2. Isolation for hard goods
Insulation against temperature changes and moisture, and defense against dust, dirt, and contamination.
3. Durability
Durable goods are made to last, and they need packaging that matches that long shelf-life. While some classic packaging materials like cardboard boxes have a good shelf-life, they are susceptible to damp and mildew and can start to decompose after long periods of time. In contrast, high performance shrink films do not degrade on the shelf and protect durable items for the length of their warehouse and shelving time.
4. Compliance for durable goods’ packaging
Packaging must comply with regulations to protect the environment from the product (such as for firearms) and the product from the environment (such as for expensive perfumes). It should be eco-friendly, sustainable, and, if possible, recyclable.
3 Differences Between Packaging for Durable Goods and Nondurable Goods
When comparing the packaging of durable goods vs nondurable goods, you can notice several differences that have more to do with product type than revenue growth:
1. Design
Consumer durable items are generally packed in simple rectangular boxes with void-filling material for protection. Consumer durables use conventional packaging designs to allow easy stacking and efficient use of warehouse space.
Nondurable goods are often irregularly shaped and come with shaped wrapping.
2. Storability
Durable goods often have longer storage times. Production may be less frequent, and the shelf life of the products is longer. Storage costs are reduced by having less bulky, lightweight, and stackable packaging that allows the best use of storage space at the minimum cost. Good packaging ensures the stacking of products without any damage.
Nondurable goods have shorter shelf lives and pass through the supply chain quickly. Packaging must be high quality but is not made to last.
3. Timing
Durables are often expensive products that are purchased infrequently; suppliers want to guarantee a memorable unboxing experience and a pleasant customer experience so that consumers will tell their friends and leave good product reviews.
Non-durables quickly wear out and are replaced, such as paper products. Users rip off the wrapping and immediately discard it.
Folene Packaging Explains the Role of Shrink Film for Durable Goods
Effective packaging serves its purpose by protecting the contents, saving expenses, and minimizing the environmental costs of the packaging footprint. Folene Packaging’s polyolefin shrink films achieve these goals by employing optimal design, user-friendliness, and using the highest quality sustainable materials.
Folene Packaging presents the Flxtite® shrink film range, which includes the Flxtite® AP-XH, well-suited to heavy-duty items like large appliances and machinery, and the Ecolene® range, a choice of environmentally friendly packaging films with 100% biodegradable shrink film and high-PCR-content shrink film options. These top-quality films can elevate your product to a new level, protecting it from water, grease, electric shock, dirt, dust, and tampering while showcasing it for optimal exposure to the consumer.
Contact Folene Packaging today and discover how our shrink-film packaging can package and protect your consumer durables.



