
Inefficient operations waste resources, including delaying product delivery and increasing operating costs. Suppliers and distributors struggle with inefficient distribution management, among other supply-chain inefficiencies, which negatively affect the movement of goods from supplier, distributor, or manufacturer to the point of sale. However, in the packaging field, lean packaging contributes to efficiency and can significantly impact operations.
Supply chain delays can cause customers to experience shortages and, ultimately, higher prices. How can businesses become more efficient? By applying lean operations, companies can conserve energy and raw materials and produce more at a lower expense. How should a company’s mission statement reflect the goal of increased efficiency? The answer is to run your business with lean management and ensure that every step meets the goals set for business excellence.
What is Lean Operations?
Lean operations means applying lean management in manufacturing and service industries. Lean management is a business strategy that drives continuous improvement. Companies that use lean management set goals to:
improve internal functions
build a productive and engaged workforce
increase profits
This is done by using tools to streamline managerial processes. One way to achieve this is by eliminating avoidable stages in the production processes and overpackaging. Some people describe the lean management method as ‘minimalist’ since running a business focuses first and foremost on improving everyday operations and overall workflow.
The Main Goals of Lean Operations Management
Companies endeavor to achieve operational excellence by applying lean operations management methods. To do so, they must understand the goals and tools of lean operations.
The main goals in lean operations management are:
To create customer value through the most effective use of resources. In a lean management system, companies avoid wasting resources and energy and produce the product in less time.
To create a workflow that meets customer needs. In lean production, businesses refine processes throughout the facility to eliminate time wasted by workers and processes. They are selective about the workforce structure.
To continuously reiterate and calculate. Lean thinking requires companies to repeat these processes and develop the lean mindset further. Calculate costs saved to measure the increased efficiencies on the company’s bottom line.
5 Benefits of Lean Operations
By changing how they work over the long term, companies see incremental improvements in processes and improve quality and efficiency.
Companies that succeed in lean operations enjoy the following benefits. They:
Run their business as efficiently as possible
Discover and eradicate hidden operational costs
Deliver value to customers without harming the company’s profit margin
Optimize internal functions and realize business benefits
They understand the business thoroughly, which allows the company to respond to customer needs faster and more efficiently.

5 Companies with Successful Lean Operations
Lean management theories translate into actual processes.
Several well-known companies have successfully implemented lean manufacturing operations:
Toyota excels by eliminating 7 types of waste and carefully planning its inventory using the Just in Time method.
Nike achieves lean operations through specific goal-setting, continuous internal structure, and process improvement. The Association for Manufacturing Excellence (AME) reports that in lean production, Nike saw productivity increase by 10%, and the time to introduce a new product to a factory was reduced by 30%.
1 Hotels used a mobile communication tool to improve guest stays and streamline processes between workers.
The Marriott hotel chain found that applying lean thinking captured higher customer satisfaction rates.
Wireless Vision uses a mobile platform to connect sales associates and campaign managers. The communication platform allows a single entry point for all 4,000 workers, making communication smoother and faster.
Bringing Lean Operations into Packaging
Lean operations are more than just a functional approach to business. As we saw with the global companies mentioned earlier, lean operations are carried into specific stages of manufacturing and business processes.
Applying the lean philosophy to packaging brings us to lean packaging and lots of potential for savings. Packaging is a key process for manufacturers since almost all products have packaging at some point in their useful life, whether it is in plastics such as polyolefins or HDPE, LDPE, cardboard, glass, or some other wrapping. This makes packaging an excellent place to apply the lean approach.
What is Lean Packaging? Do More With Less
Lean packaging refers to using a focused process and eliminating waste in elements of the packaging process. This means reducing stages that do not add value to the manufacturer and the customer. Lean packaging requires thinking outside the box, using innovative techniques, and a dedication to continuous improvement. To define lean operations, you do more with less and use resources efficiently while providing the greatest value.
In the lean approach, wastefulness is negative, and efficiency is positive. So, lean packaging could be called ‘efficiency in packaging’ or maybe ‘packaging kaizen‘ (Japanese for a change for the better). Bringing lean operations into packaging is packaging optimization, but it focuses on a different angle from other types of waste reduction. Having said that, lean packaging does work alongside the newly passed Packaging Reduction and Recycling Infrastructure Act (PRRIA).
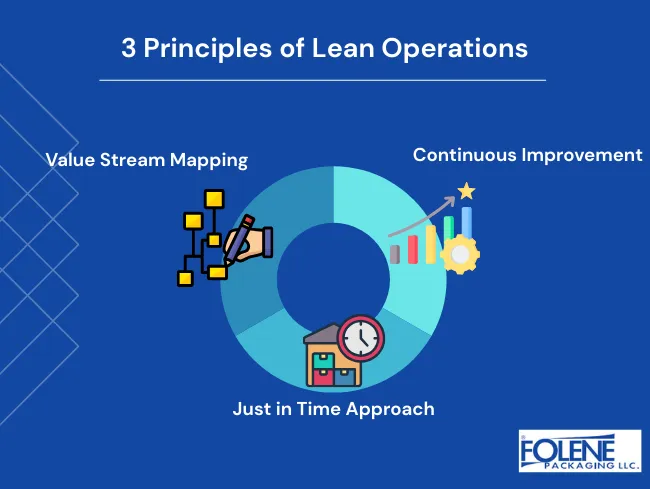
3 Principles of Lean Packaging – Foundational Pillars
In Packaging Gateway, the B2B network offering insights into the packaging industry, Oumar Fofana shares 3 principles for achieving lean packaging. These principles are:
Value stream mapping: This is where the producer visualizes the packaging process, from the very beginning to the end, from the raw components to the end of the useful life of the packaging, and pinpoints zones of waste and inefficiency. The producer can then target bi-directional strategies that effectively eliminate waste while enhancing value.
The just in time approach: Supply is at the point of packaging (e.g., manufacturers or distributors that repackage goods or divide apples from bushels to prepacked trays for individual consumers), and producers avoid stockpiling packaging inventory. Packaging supplies are ordered to arrive just in time (JIT) for when they are needed. Production lines produce only what is needed, just when they need it. Suppliers of packaging needs must have a large stock of raw materials ready and waiting for customer demand, thereby minimizing excess inventory and reducing the risk of obsolescence.
Continuous improvement: The ultimate goal of lean operations is to have an impact on efficiency, to use new opportunities for improvement, and to remove inefficiency. Simultaneously, businesses can adapt to reduce their carbon footprint and meet sustainability goals while meeting other business goals.
An Example of Applied Lean Packaging
FastCap, a supplier of woodworking tools and products, created a short video demonstrating how packaging time was reduced to 1 minute using lean packaging principles – while giving the customer a cleaner, more professional-looking package.

10 Business Advantages of Lean Packaging
Lean packaging impacts businesses in many helpful ways, and the benefits are currently being recognized increasingly.
Some of the advantages of the lean manufacturing system for packaging are:
1. Lean operations help businesses gain better lead times
Save the time it takes to produce items by streamlining workflows
2. Save time-to-market with the lean manufacturing system
Deliver products more quickly and reliably by applying JIT principles from the raw material stage to delivery of products to customer in appropriate delivery packaging, avoiding overpackaging.
3. Boost more profits with lean operations principles
Over time, the cost savings are often significant, noticeably growing the profit margin
4. Creating a lean culture drives customer satisfaction
Enhance productivity via improvements in quality control measures and reliability of packaging. Companies can reduce defects due to poor packaging and get fewer consumer complaints
5. Generate enhanced quality by applying lean manufacturing principles
Make high-quality standards. Standardize production and packaging processes for increased product quality the first time without expending excess energy.

6. Use the lean culture to increase responsiveness to customer needs
Producers can be responsive to evolving customer demands through lean inventory management and delivery options such as single-unit packaging for e-commerce orders (which effectively avoids e-commerce overpackaging).
7. A lean culture encourages businesses to maximize process efficiency
Making the most of groundbreaking internal processes and communication platforms allows businesses to optimize all processes, pursuant to the principles of lean operations.
8. Facilitate waste reduction with lean packaging
Eliminate waste of physical resources and avoidable work hours after identifying what adds value and what doesn’t. Individual workers are encouraged to grow in their professional development as part of capturing opportunities for improvement.
9. Leverage lean operations to continuously reduce costs
Perform cost reduction analysis throughout the production: raw materials, labor expenses, storage costs of components and finished products
10. Address environmental concerns by creating a lean culture
Companies can offer more sustainable solutions by using less packaging materials and resources wherever possible in their business and utilizing readily available resources with low-energy requirements to produce. Businesses meet their own goals and build customer loyalty.
How Folene Packaging Helps You Apply Lean Operations to Packaging
Folene Packaging professionals understand the source of the raw materials and end destination of all shrink-wrap types in the Flxtite® and Ecolene® range over the entire lifecycle of the shrink wrap. This means we can advise you on which product best suits your needs. With careful planning and advice, manufacturers can apply lean manufacturing principles to packaging and enjoy resource savings and benefits. Folene Packaging also helps you avoid waste and inefficiency in your packaging by offering different sizes and gauges of shrink wrap. Choose the size and type you need. Additionally, by using shrink wrap, you can avoid wasting storage and delivery space on large cardboard boxes.
Folene Packaging can fulfill local US orders very quickly (as low as a 2-day turnaround time), which supports JIT principles. With such quick delivery capabilities, our clients don’t need to stock up on more packaging material than they need – saving dollars that would otherwise be consumed as warehouse and storage costs.
Contact Folene Packaging today to learn how you can incorporate lean operations into your manufacturing or distribution facility.
Lean Operations FAQs
How can companies measure success in applying lean operations?
After allowing a reasonable amount of time to set up and implement the lean culture, companies can track improvements in these areas: (1) identify and measure KPIs (key performance indicators), some of which are productivity levels, cycle times, lead times, overall efficiency, and customer satisfaction; (2) set clear goals; (3) regularly review progress and determine whether the activities are doing what you want them to do. It is advisable to share information with key stakeholders to encourage participation and support for lean operations.
What does lean manufacturing mean?
Lean manufacturing is the application of lean operation principles to manufacturing. In lean manufacturing, the entire production process is based on lean principles to maximize productivity and minimize waste using the 5 lean principles. The 5 principles of Lean were established in the automotive industry by Toyota (the Toyota Production System) to streamline operations, but were originally demonstrated by Henry Ford, who initiated production efficiency; they include: (i) identifying core value in your product or system, (2) mapping its value stream, (3) creating a production flow, (4) inaugurating a pull system, and (5) ensuring continuous improvement.



